Just Published in Angewandte Chemie, International Edition
09/12/2017Reversible Oxidative Addition at Carbon
Authors: Antonius F. Eichhorn, Sonja Fuchs,Marco Flock, Prof. Dr. Todd B. Marder, Prof. Dr. Udo Radius
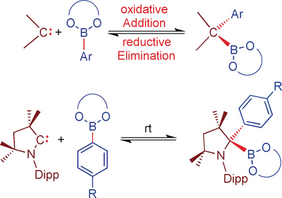
Abstract: The reactivity of N-heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs) and cyclic alkyl amino carbenes (cAACs) with arylboronate esters is reported. The reaction with NHCs leads to the reversible formation of thermally stable Lewis acid/base adducts Ar-B(OR)2⋅NHC (Add1–Add6). Addition of cAACMe to the catecholboronate esters 4-R-C6H4-Bcat (R=Me, OMe) also afforded the adducts 4-R-C6H4Bcat⋅cAACMe (Add7, R=Me and Add8, R=OMe), which react further at room temperature to give the cAACMe ring-expanded products RER1 and RER2. The boronate esters Ar-B(OR)2 of pinacol, neopentylglycol, and ethyleneglycol react with cAAC at RT via reversible B−C oxidative addition to the carbene carbon atom to afford cAACMe(B{OR}2)(Ar) (BCA1–BCA6). NMR studies of cAACMe(Bneop)(4-Me-C6H4) (BCA4) demonstrate the reversible nature of this oxidative addition process.
Link: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.201701679/abstract


![[Translate to Englisch:] [Translate to Englisch:]](/fileadmin/_processed_/d/f/csm_FrontICBC2_1dbc3f66ed.jpg)
![[Translate to Englisch:] [Translate to Englisch:]](/fileadmin/_processed_/4/c/csm_IAC_Back_958d8b320b.png)