Ribozymes
RNA-catalyzed RNA methylation
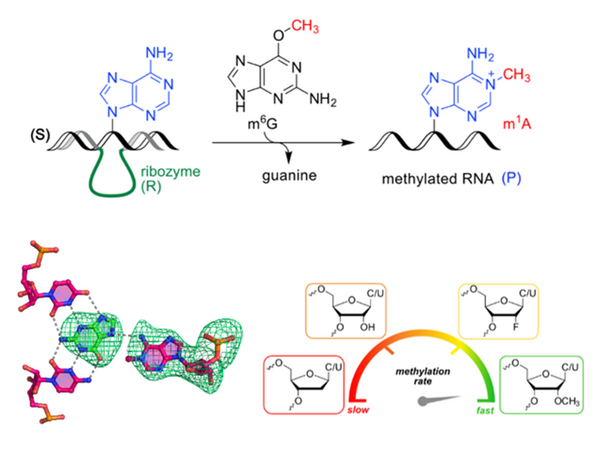
Using O6-methylguanine (m6G) as methyl group donor, we recently discovered the first methyltransferase ribozyme (MTR1), which catalyzes a site-specific intermolecular methyl transfer reaction to generate the native methylated nucleotide 1-methyladenosine m1A. Surprisingly, the structure revealed a cofactor binding site reminiscent of natural purine riboswitches. We found that the catalytic mechanism involves specific nucleobase protonation, and discovered a synergistic effect of two methylated ribose residues in the active site, suggesting that modified nucleotides may have enhanced early RNA catalysis.
Publications on this topic:
C.P.M. Scheitl, M. Ghaem Maghami, A.-K. Lenz, C. Höbartner
Site-specific RNA methylation by a methyltransferase ribozyme
Nature 2020, 587, 663–667
C.P.M. Scheitl, M. Mieczkowski, H. Schindelin, C. Höbartner
Structure and mechanism of the methyltransferase ribozyme MTR1
Nat. Chem. Biol. 2022, 18, 547–555
T. Okuda, A.-K. Lenz, F. Seitz, J. Vogel, C. Höbartner.
A SAM analogue-utilizing ribozyme for site-specific RNA alkylation in living cells
Nat. Chem. 2023, 15, 1523–1531
RNA-catalyzed RNA labeling
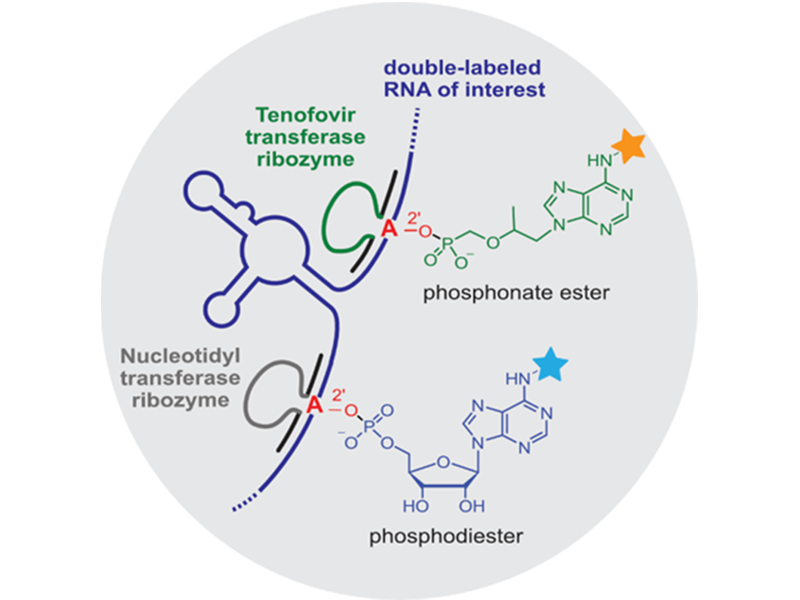
Inspired by natural guide RNAs, which direct protein enzymes sequence-specifically to their targets by Watson-Crick base pairing, we developed ribozymes that covalently ligate bioorthogonal nucleotides to the 2’-OH group of a target nucleotide flanked by the Watson-Crick binding arms. We have shown that suitably derivatized antiviral nucleoside analogues can be repurposed as ribozyme substrates and allow site-specific labelling in the context of total cellular RNA.
Publications on this topic:
M. Ghaem Maghami, C.P.M. Scheitl, C. Höbartner,Direct in vitro selection of trans-acting ribozymes for posttranscriptional, site-specific, and covalent fluorescent labeling of RNA J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 19546-19549.
M. Ghaem Maghami, S. Dey, A.-K. Lenz, C. Höbartner, Repurposing antiviral drugs for orthogonal RNA‐catalyzed labeling of RNA Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 9335–9339. Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 9421-9425.
C. P. M. Scheitl, T. Okuda, J. Adelmann, C. Höbartner
Ribozyme-Catalyzed Late-Stage Functionalization and Fluorogenic Labeling of RNA
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2023, 62,e202305463. Epub 2023 Jun 23