Research
Molecular design
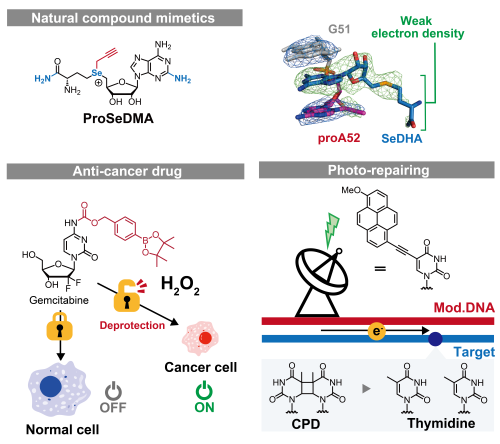
Molecular design in our lab focuses on extending what RNA can do by integrating knowledge of organic chemistry.
We create molecules with specific functions—such as nucleic acids bearing fluorescent dyes for imaging and analytics, or conjugates endowed with anticancer activity. Designs often build on natural metabolites and cofactors: by introducing tailored, bio-orthogonal modifications, these hybrids can make effective use of cellular pathways to deliver the intended activity. Structure–activity relationships and modular synthesis guide each iteration from concept to working construct.
Selected Publications on this topic:
A SAM analogue-utilizing ribozyme for site-specific RNA alkylation in living cells. Nature Chemistry, 15, 1523–1531. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-023-01320-z
Inhibiting guanine oxidation and enhancing excess-electron- transfer efficiency of a pyrene-modified oligonucleotide by introducing an electron-donating group on pyrene: Chem. Comm., 55, 14062–14065. https://doi.org/ 10.1039/c9cc06498b
A Hydrogen Peroxide Activatable Gemcitabine Prodrug for the Selective Treatment of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: ChemMedChem, 14, 1384–1391 (Front Cover). https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.201900324
Molecular evolution
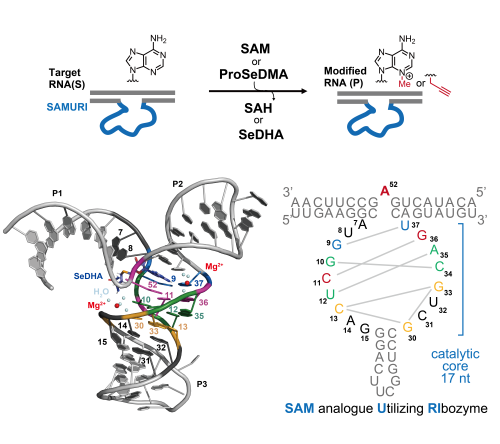
Molecular evolution is a powerful strategy for discovering catalytic RNAs.
Large, diverse RNA libraries undergo iterative selection and amplification, progressively yielding sequences that perform a defined function under tightly controlled conditions. By incorporating custom cofactors designed in our lab, these strategies reveal ribozymes with activities not observed in nature. The resulting catalysts are characterized by X-ray crystallography, next-generation sequencing (NGS), and LC–MS to resolve structure–activity relationships and uncover hidden RNA functions.
Selected Publications on this topic:
Structure and catalytic activity of the SAM utilizing ribozyme SAMURI. Nature chemical biology, Published online January 8, 2025. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-024-01808-w
A SAM analogue-utilizing ribozyme for site-specific RNA alkylation in living cells. Nature Chemistry, 15, 1523–1531. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-023-01320-z
tRNA as an assembly chaperone for a macromolecular transcription-processing complex: Nature structural & molecular biology. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41594-025-01653-y