MRI-Kontrastmittel
MRI Contrast Agents
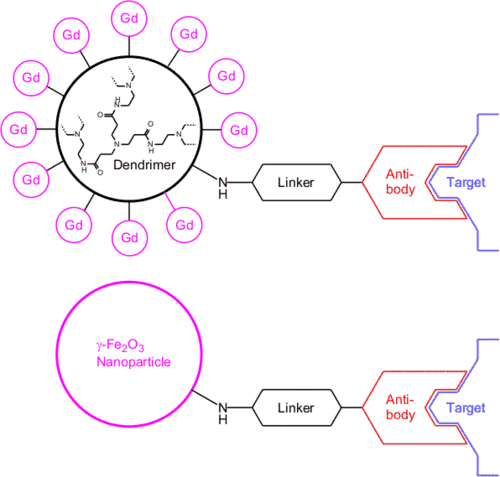
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has a number of advantages which make it the most versatile medical imaging modality: High spatial resolution, no known radiation risk, and the opportunity to tune both the contrast agents (either Gd-based or iron oxide-based) and the recording parameters to a host of different applications. However, for the purposes of molecular imaging, i.e. the detection of molecular epitopes, there is still a lack of sensitivity, even at the highest field strengths available today. This problem might be overcome by linking the antibody, which is designed to home in on the target in question, through a dendrimer or polymer with a large number of Gd ions. Similarly, it should be possible to tie antibodies to magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. In a collaboration within the Sonderforschungsbereich 688 we are currently pursuing both strategies.